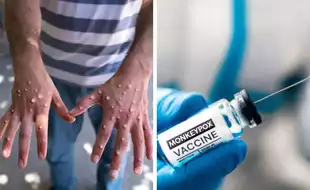
The latest drug-resistant Mpox cases follow an initial, unrelated cluster reported in California in early 2023 and are the first involving multiple states
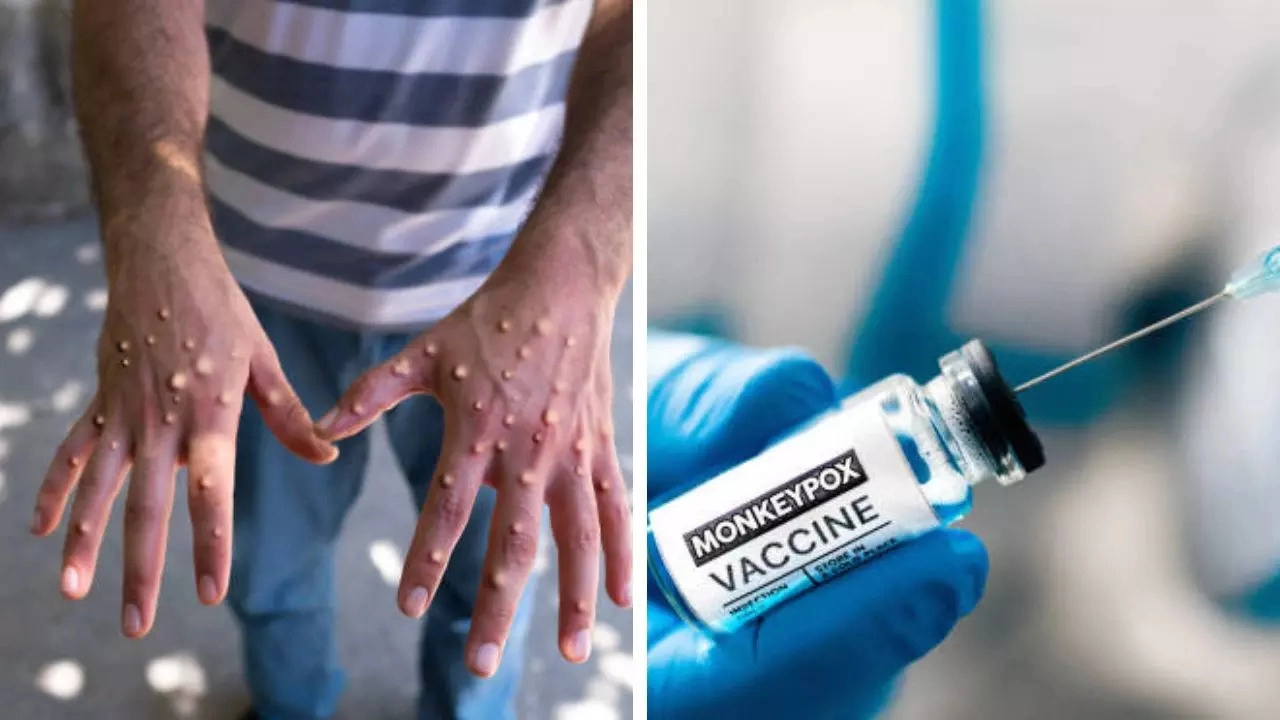
US health officials say they have identified a cluster of cases caused by a variant of the highly dangerous Mpox virus, which is to Siga Technologies' antiviral tecovirimat, branded as TPOXX, in five states.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, at least 18 people were infected with Clade II Mpox between October 6, 2023, and February 15, 2024 – and none of them had ever taken the treatment before. Experts say the Clade II Mpox cases are endemic to West Africa – which sparked a global outbreak in 2022 and this year prompted the World Health Organization to declare a public health emergency.
Mpox cases continue to spread at low levels in many countries, especially in the DR Congo.
An earlier cluster was reported in California last year
The report says these drug-resistant Mpox cases follow an initial, unrelated cluster reported in California in early 2023 and are the first involving multiple states. Health officials said the latest cases were not taken seriously earlier because all the Mpox cases do not undergo genetic sequencing to determine the variant that leads to the infection.
According to the study authors, round-the-clock surveillance is needed to monitor the emergence of drug resistance to safeguard the effectiveness of TPOXX - the antiviral drug stockpiled for smallpox preparedness. It is also used for the treatment of other orthopoxvirus infections, including Mpox.
The report says CDC officials have advised doctors to closely follow the protocol for the use of TPOXX, and make sure that patients take the drug properly. The findings also underscore the need for additional Mpox treatments.
What is the clade II strain of Mpox?
Three clades of the Mpox virus are recognized by the WHO - Clade I is present in the Congo Basin and causes up to 10 per cent human mortality. It is usually transmitted through rodents with little human-to-human spread. Clade II is there in West Africa – and has a low mortality rate.
Experts say, Clade IB is more transmissible than clade II and capable of being more severe, so infectious disease experts are concerned about further international spread.
US evaluating the use of TPOXX in Clade 1B cases
According to the report, the study evaluated the use of TPOXX in Clade 1B cases with the results that treatment was not effective at helping patients recover more quickly than a dummy treatment.
Mpox is a viral infection that causes flu-like symptoms and pus-filled lesions. Although usually mild, the virus can be deadly in some individuals with weakened immune symptoms. Mpox is transmitted through close physical contact, including sexual contact.
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world.