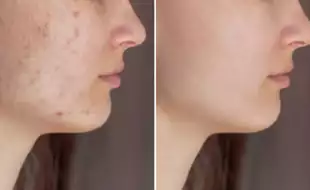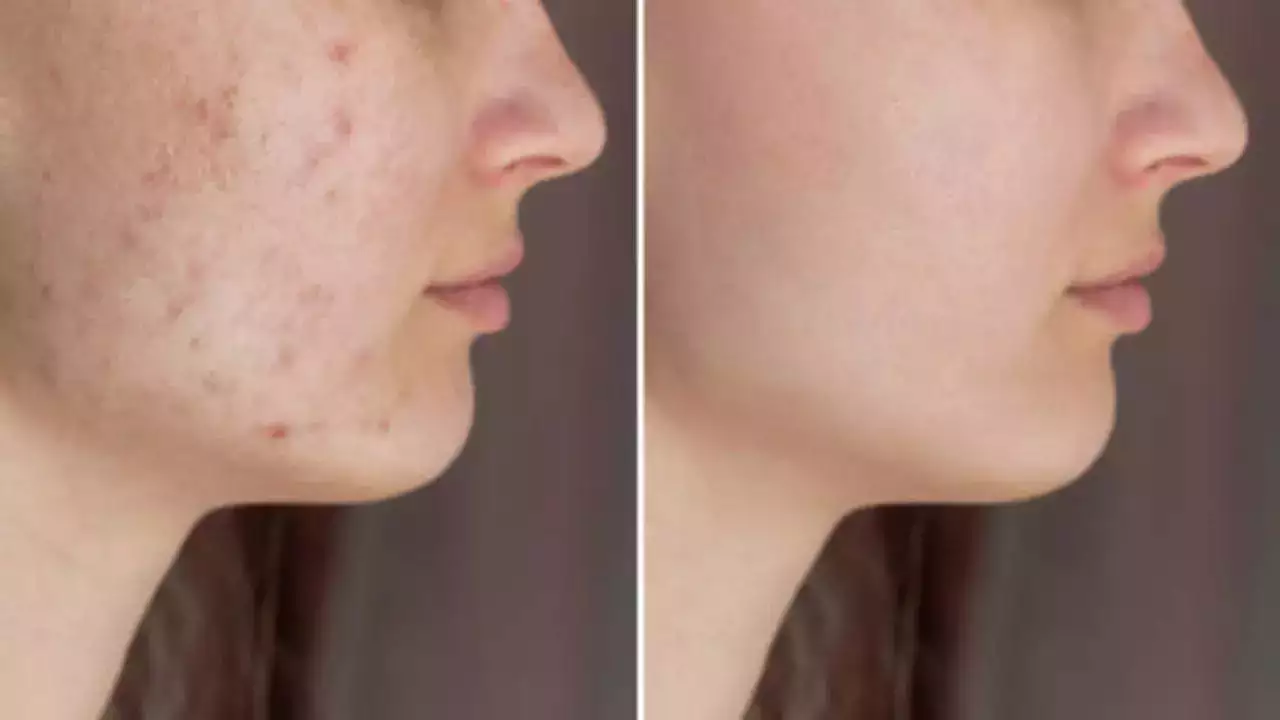
Sun, Stress, Or Screens? What’s Really The Cause Behind Melasma- Expert Answers (Image Credits: iStock, Image for representation)
Have you ever noticed dark patches appearing on your cheeks, forehead, or upper lip, especially after spending time in the sun? You might be dealing with melasma, a common skin condition often referred to as "the mask of pregnancy" or chloasma. While it’s not harmful, it can be distressing for those who experience it. But why does it happen, and how can you prevent or treat it? We got in touch with Dr Chandani Jian Gupta, MBBS, MD-Dermatology and Aesthetic Physician at Elantis Healthcare, New Delhi, to break it down.
What Causes Melasma?
Melasma is caused by an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for the colour of the skin, hair, and eyes. Several factors contribute to this excess melanin, which leads to dark patches on the skin.
1. Hormonal Imbalances
According to Dr Gupta, hormonal changes play a major role in triggering melasma. "Fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels stimulate melanocytes—the pigment-producing cells in the skin—to produce excess melanin," she explains. This is why melasma is often seen in:
- Pregnant women – Due to elevated hormone levels, many women develop what’s known as the "pregnancy mask."
- Those on birth control pills or hormone therapy – Hormonal contraceptives can lead to pigmentation changes.
- People with thyroid disorders – An underactive or overactive thyroid can trigger skin pigmentation.
2. Sun Exposure and UV RadiationOne of the biggest culprits behind melasma is sunlight. "UV rays stimulate melanocytes, leading to increased pigmentation," says Dr Gupta. "Even brief sun exposure can worsen melasma, especially if proper sun protection isn't used." Surprisingly, even indoor lights—such as the blue light from screens—can contribute to worsening melasma over time.
3. Genetics And Skin Type
If your parents or siblings have melasma, you may be genetically predisposed to developing it. Further, darker skin tones are more prone to melasma since their melanocytes are naturally more active.
4. Stress And Lifestyle Factors
Stress can also be a hidden trigger. "High stress levels lead to an increase in cortisol, which indirectly affects melanin production," Dr Gupta notes. Poor skincare habits, like using harsh products or skipping sunscreen, can further worsen melasma.
How to Treat & Prevent Melasma
While melasma is stubborn, it can be managed with consistent care. Here’s what dermatologists recommend:
- Use Sunscreen Daily – "A broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher is a must," advises Dr Gupta. "Apply it even when indoors, as light from screens and bulbs can contribute to melasma."
- Protect Your Skin – Hats, sunglasses, and umbrellas aren’t just fashion accessories—they provide essential protection against UV rays.
- Topical Treatments – "Dermatologists may prescribe creams containing hydroquinone, retinoids, or vitamin C to lighten pigmentation," Dr. Gupta explains. Natural ingredients like liquorice extract and niacinamide also help in reducing dark patches.
- Professional Treatments – If melasma is severe, procedures like chemical peels, laser therapy, or microdermabrasion can help. However, Dr Gupta warns that not all treatments suit every skin type, so consulting a specialist is key.
Melasma isn’t dangerous, but it can impact confidence. The good news? With proper sun protection, skincare, and expert treatments, you can manage and even fade melasma over time. If you're struggling with persistent pigmentation, consulting a dermatologist is the best step toward clear, healthy skin.
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world.